K-Fold Cross Validation
Source: K-Fold Cross Validation Technique and its Essentials
What is K-Fold Cross Validation?
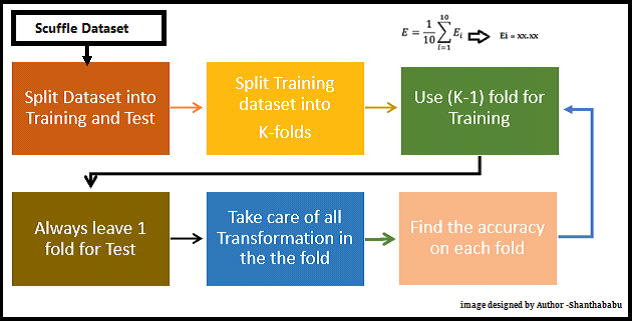
K-fold cross-validation is a technique for evaluating predictive models. The dataset is divided into k subsets or folds. The model is trained and evaluated k times, using a different fold as the validation set each time. Performance metrics from each fold are averaged to estimate the model’s generalization performance. This method aids in model assessment, selection, and hyperparameter tuning, providing a more reliable measure of a model’s effectiveness.
In each set (fold) training and the test would be performed precisely once during this entire process. It helps us to avoid overfitting. As we know when a model is trained using all of the data in a single short and give the best performance accuracy. To resist this k-fold cross-validation helps us to build the model is a generalized one.
To achieve this K-Fold Cross Validation, we have to split the data set into three sets, Training, Testing, and Validation, with the challenge of the volume of the data.
Here Test and Train data set will support building model and hyperparameter assessments.
In which the model has been validated multiple times based on the value assigned as a parameter and which is called K and it should be an INTEGER.
Make it simple, based on the K value, the data set would be divided, and train/testing will be conducted in a sequence way equal to K time.
Life Cycle of K-Fold Cross-Validation
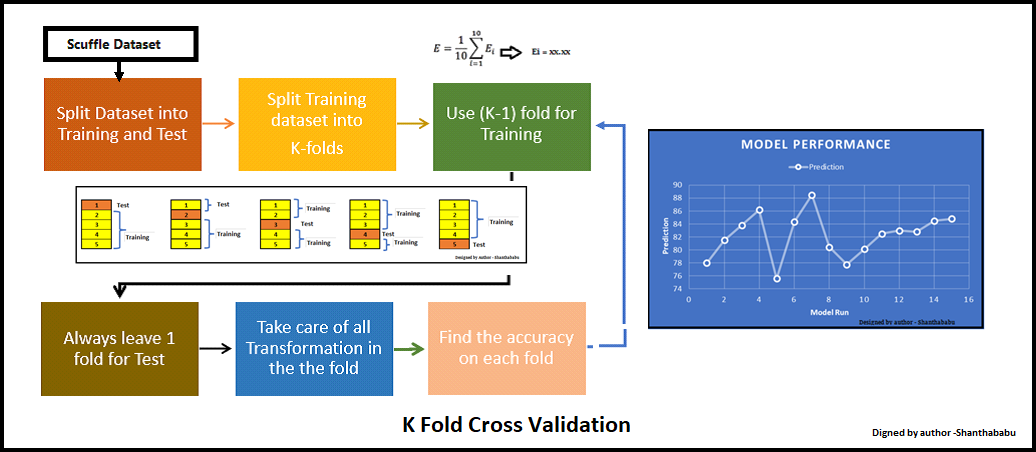
Let’s have a generalised K value. If K=5, it means, in the given dataset and we are splitting into 5 folds and running the Train and Test. During each run, one fold is considered for testing and the rest will be for training and moving on with iterations, the below pictorial representation would give you an idea of the flow of the fold-defined size.
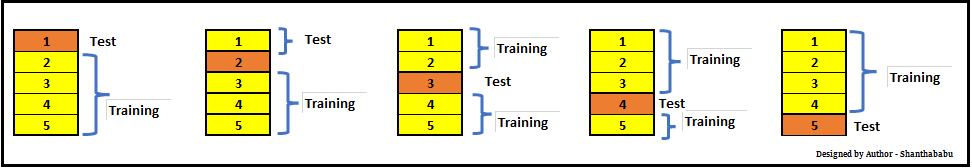
In which each data point is used, once in the hold-out set and K-1 in Training. So, during the full iteration at least once, one fold will be used for testing and the rest for training.
In the above set, 5- Testing 20 Training. In each iteration, we will get an accuracy score and have to sum them and find the mean. Here we can understand how the data is spread in a way of consistency and will make a conclusion whether to for the production with this model (or) NOT.
Model Selection using K-Fold
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
digits = load_digits()
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(digits.data,digits.target,test_size=0.3)
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is k-fold cross-validation value?
A. K-fold cross-validation is a technique used in machine learning and statistical modeling to evaluate the performance of a predictive model. It involves dividing the dataset into k subsets or folds of approximately equal size. The model is then trained and evaluated k times, each time using a different fold as the validation set and the remaining folds as the training set. The performance metrics obtained from each fold are averaged to provide a more robust estimate of the model’s generalization performance. Common values for k are 5 and 10, but other values can also be used depending on the dataset size and complexity.
Q2. How do you use K-fold cross validation?
A. K-fold cross-validation is used to assess the performance of a machine learning model and to estimate its generalization ability. Here are the steps to utilize K-fold cross-validation:
- Split the data: Divide your dataset into k equal-sized subsets (folds). Typically, k is chosen as 5 or 10, but you can adjust it based on your needs.
- Train and validate: Iterate over the k folds. In each iteration, use k-1 folds for training the model and the remaining fold for validation. Train your model on the training folds and evaluate its performance on the validation fold.
- Performance metrics: Calculate the performance metric(s) of interest (e.g., accuracy, precision, recall) for each fold. These metrics quantify how well the model generalizes to unseen data.
- Average the results: Average the performance metrics obtained from the k folds to obtain a more robust estimate of the model’s performance. This average value represents the overall performance of the model.
- Model selection and tuning: Based on the cross-validation results, you can compare different models or hyperparameter settings and select the one that performs the best on average across the folds.
- Final evaluation: After selecting the model or hyperparameters, you can retrain the model using the entire dataset and evaluate its performance on a separate test set to obtain a final performance estimation. K-fold cross-validation helps to mitigate the risk of overfitting and provides a more reliable assessment of how well the model is expected to perform on unseen data.
Conclusion
Guys! so far, we have discussed various aspects of the K-Fold Cross Validation Technique and its importance in the Machine Learning model for production, parameter selection with a classical example. I trust this article would help you all to understand this topic better. If you ask me if we have any disadvantages of this, my answer would be Yes! That is nothing but slow in execution than straightforward training and test. In spite of this small drawback, K Fold cross-validation plays a critical role in the Machine Learning world.